Midazolam (Versed) Addiction and Abuse

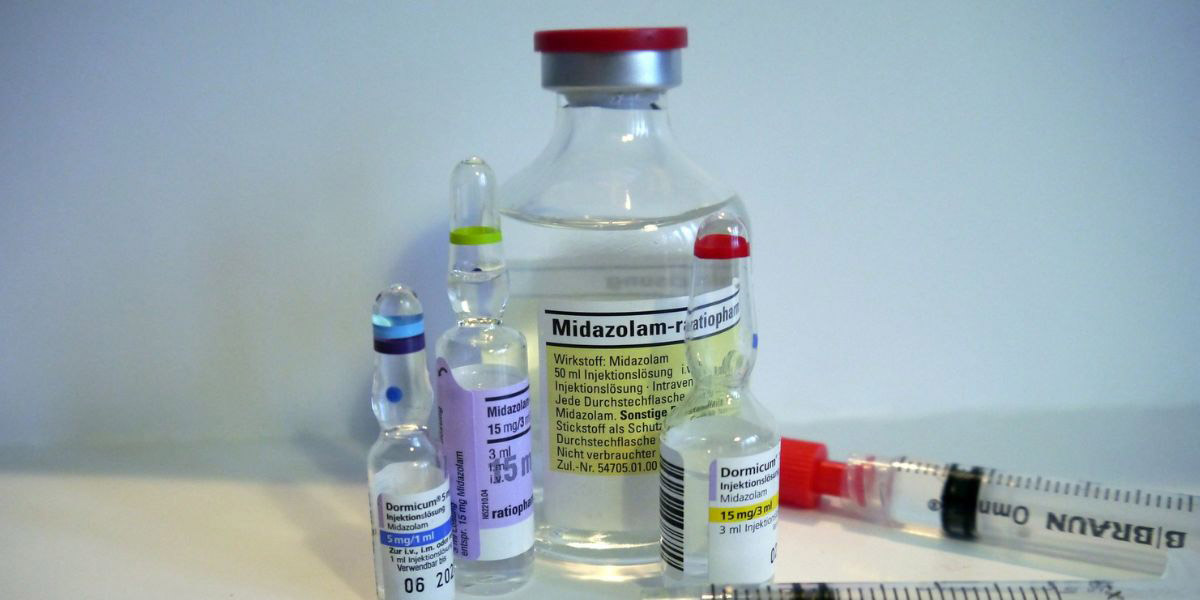
Midazolam, commonly known by its brand name Versed, belongs to a class of medications called benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines are prescription drugs used for their sedative properties and to reduce anxiety. While midazolam is essential in medical settings, it has a high potential for abuse and addiction. This has raised concerns among healthcare professionals.
What Is Midazolam (Versed)?
Midazolam (Versed) is a prescription medication in the benzodiazepine family of medicines, widely used for its sedative effects. It is primarily administered in medical settings to induce sedation before procedures, for anesthesia induction, and for managing severe anxiety. Midazolam enhances the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits activity in the central nervous system, leading to relaxation and sedation.
Midazolam can be administered in various forms, including oral tablets, injections, intravenous infusions, and a syrup called midazolam HCL. Its rapid onset and short duration of action make it particularly useful in surgical and diagnostic procedures. However, these same properties also contribute to its potential for misuse and abuse.
This drug is easy to access and has strong effects. People are attracted to it because they can get high without medical supervision.
What Are the Effects of Versed?
Versed exerts its effects by acting on the central nervous system, producing a range of short-term effects. When taken as prescribed for medical purposes, midazolam can effectively calm anxiety, induce sleep, and cause muscle relaxation. The desired effects of medical procedures include sedation, amnesia (loss of memory during the procedure), and reduction of anxiety.
However, when misused or in higher doses than prescribed, the effects of Versed can be dangerously intensified. The euphoric and calming effects can happen when people misuse the drug, often resulting in addiction. Users may feel relaxed and sleepy, with less anxiety. However, they may also have trouble breathing and other serious side effects.
Mixing midazolam with alcohol or opioids can increase its effects and be dangerous. This combination can lead to issues such as difficulty breathing, which could potentially be life-threatening. This dangerous interaction highlights the need for careful monitoring and adherence to prescribed dosages.

Midazolam Side Effects
While midazolam is effective in its intended uses, it comes with a range of side effects that can vary in severity. Common side effects include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Nausea, vomiting
- Headache
- Fatigue
In some cases, more severe side effects can happen, especially when midazolam is misused or taken in higher doses than prescribed. These severe side effects include:
- Respiratory depression
- Trouble breathing
- Low blood pressure
- Confusion
- Agitation
- Aggressive behavior
- Hallucinations
The risk of experiencing these side effects increases with higher doses and prolonged use. This underscores the importance of using midazolam strictly as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
People with respiratory conditions or those taking central nervous system depressants should take special precautions. They are more likely to experience severe side effects. Healthcare providers must thoroughly evaluate patients before prescribing midazolam, considering their medical history and potential risk factors.
Long-Term Side Effects of Midazolam Abuse
The long-term abuse of midazolam can lead to serious health complications. Chronic misuse of Versed can result in both physical and psychological dependence, often leading to a substance use disorder. Long-term side effects of midazolam abuse include:
- Development of tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects
- Physical dependence, leading to withdrawal symptoms when you’re not using the drug
- Cognitive impairment, including memory loss and difficulty concentrating
- Respiratory problems, including chronic difficulty breathing and respiratory depression
- Cardiovascular issues, such as low blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms
- Mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, and mood swings
- Organ damage, such as harm to your kidney or liver
It is important to monitor the use of midazolam. Addiction treatment should be provided when needed.
Long-term use can greatly impact a person’s quality of life. It can lead to poor physical health, strain relationships, and make daily tasks more difficult. Intensive care and early intervention are crucial to prevent these risks and support people in recovery.
Midazolam (Versed) Addiction Treatment
Addiction to midazolam requires a comprehensive treatment approach to address both the physical dependence and the underlying psychological factors contributing to the addiction. Treatment for midazolam addiction typically includes:
Medical Detox
The first step in treating midazolam addiction is medical detox. This process involves tapering, which is gradually reducing the dosage of the drug under medical supervision to minimize withdrawal symptoms safely. Withdrawal symptoms from benzodiazepines like midazolam can be severe, with symptoms including:
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Seizures
- Tremors
- Sweating
- Irritability
Medical detox is important because it keeps the person safe during withdrawal. This lowers the chances of serious problems. These problems include seizures and extreme anxiety.
Medical professionals should conduct the detox process in a controlled environment where they can provide immediate care. This setting allows for managing complications during detox, ensuring the person’s safety and comfort.
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is an essential component of addiction treatment. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps people identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to substance abuse. Therapy can help with mental health issues like anxiety and depression that often occur in people addicted to midazolam. Other therapeutic approaches, such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) and motivational interviewing, can also be beneficial in addressing the psychological aspects of addiction.

Support Groups
Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or other peer support groups, provide a community of people who are also recovering from addiction. These groups offer emotional support, encouragement, and accountability, which are crucial for long-term recovery.
Being in these groups can provide valuable support and encouragement to people overcoming obstacles. This is due to the shared experiences and wisdom that members bring to the table. These groups can help people recover by offering perspective and guidance. The sense of community and understanding within these groups can be a source of motivation for those facing challenges.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
In some cases, medication-assisted treatment may be used to manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. Doctors may give antidepressants or anti-anxiety meds to help stabilize a person during their recovery. Certain medications can help block the effects of benzodiazepines, which can prevent relapse and support long-term recovery.
Ongoing Aftercare
Addiction recovery is an ongoing process that requires continuous support and care. Aftercare programs, including continued therapy, support group participation, and regular check-ins with healthcare providers, are essential for maintaining sobriety and preventing relapse.
Aftercare involves making lifestyle changes such as exercising regularly, eating healthily, and finding new hobbies to replace substance use. These changes can help support recovery and maintain overall well-being.
Regular exercise can improve physical health and mental well-being. Eating a balanced diet can provide essential nutrients for the body to function correctly. Engaging in new hobbies can provide a positive outlet for stress and boredom. Building a solid support network and engaging in healthy activities can significantly enhance the chances of long-term recovery.
If you or a loved one is addicted to midazolam, White Oak Recovery Center (WORC) can provide personalized treatment. The center offers care and support for those struggling with addiction.
You can trust White Oak Recovery Center to help you or your loved one overcome addiction to midazolam. Our individualized approach to substance abuse treatment is designed to meet each person’s individual needs.
WORC only uses evidence-based treatments and therapies at White Oak Recovery Center. These help us address the underlying causes of addiction. We also focus on any mental health issues that may be present.
WORC is a residential treatment center with devoted, licensed, and experienced staff that create an empowering, nurturing environment. In our medical detox program, we help you create a treatment plan and aftercare plan for your safety and well-being. We work together to ensure your health and recovery. Our goal is to support you in maintaining your well-being after detox.
Our treatment specialists are eager to help you start a life rooted in recovery. Contact us today.

Am I covered for addiction treatment?
Your insurance may cover treatment. Call now for an entirely free and confidential assessment. Recovery starts with a phone call.

- Lingamchetty, Thejasvi N., et al., “Midazolam.” StatPearls: National Library of Medicine, Jun. 2023.
- “Midazolam.” National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Jun. 2023.
- Bauer, L.O., et al., “Chronic Alcohol Abuse and the Acute Sedative and Neurophysiological Effects of Midazolam.” Psychopharmacology (Berl)., Oct. 1997.
- Pinheiro Coroa, Maria Claudia, et al., “What Is Known About Midazolam? A Bibliometric Approach of the Literature.” Healthcare (Basel)., Dec. 2022.
- Reves, J.G., “Midazolam: Pharmacology and Uses.” Anesthesiology, Mar. 1985.
Medical Disclaimer:







